When developing a brand identity, understanding how marketing and design come together is crucial for brand success, as you’ll deal with logo design, color palettes and marketing campaigns. With logos, you’ll be using vector graphics, whereas with your print advertisements, you’ll be using raster images.
As a visual artist, it’s crucial to be comfortable with different file formats and mediums to convey your design in the most effective way possible. Knowing the differences between raster vs. vector file formats will help you understand when to use each one and for what purpose.
Let’s dive into raster vs. vector differences, pros, cons, and how to convert your file formats. Whether you’re editing photos or creating new icons, you’ll be prepared for your next creative undertaking.
Table of Contents:
- What’s the Difference Between Vector and Raster Images?
- What Is a Raster Image?
- What Is a Vector Image?
- Pros and Cons of Raster Images
- Pros and Cons of Vector Images
- How To Convert Raster to Vector
- How To Convert Vector to Raster
What’s the Difference Between Vector and Raster Images?
Before jumping into how raster and vector formats work, let’s run through some key terminology.
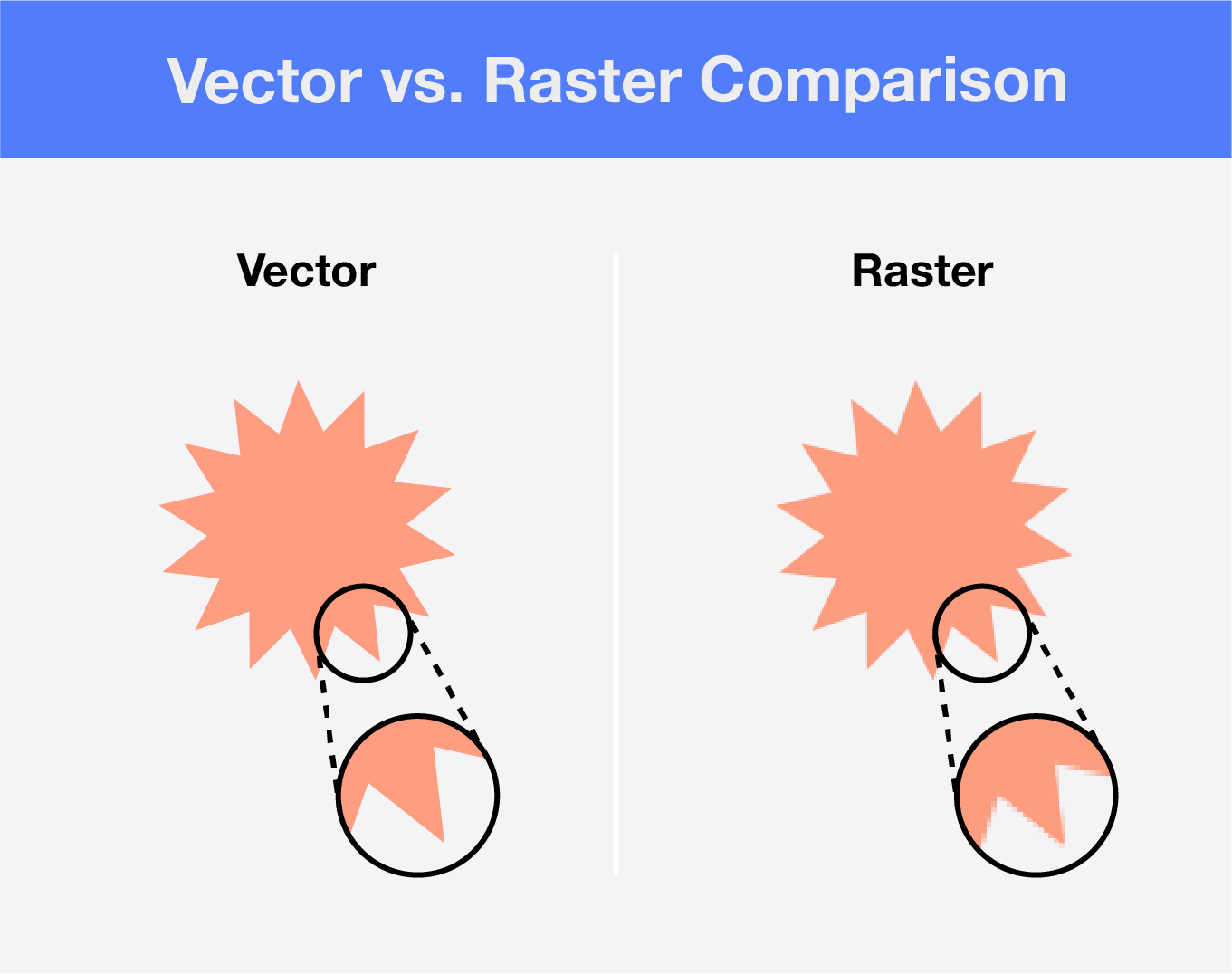
With raster images, you’re dealing with pixels. Pixels are tiny square dots that utilize tones and colors to produce an image, like a photograph. A collection of pixels is referred to as a bitmap.
With vector images, you’ll utilize mathematical formulas made up of lines, curves and dots that allow your drawn-out elements to scale proportionally. These points are referred to as coordinates, whereas the curves are referred to as paths.
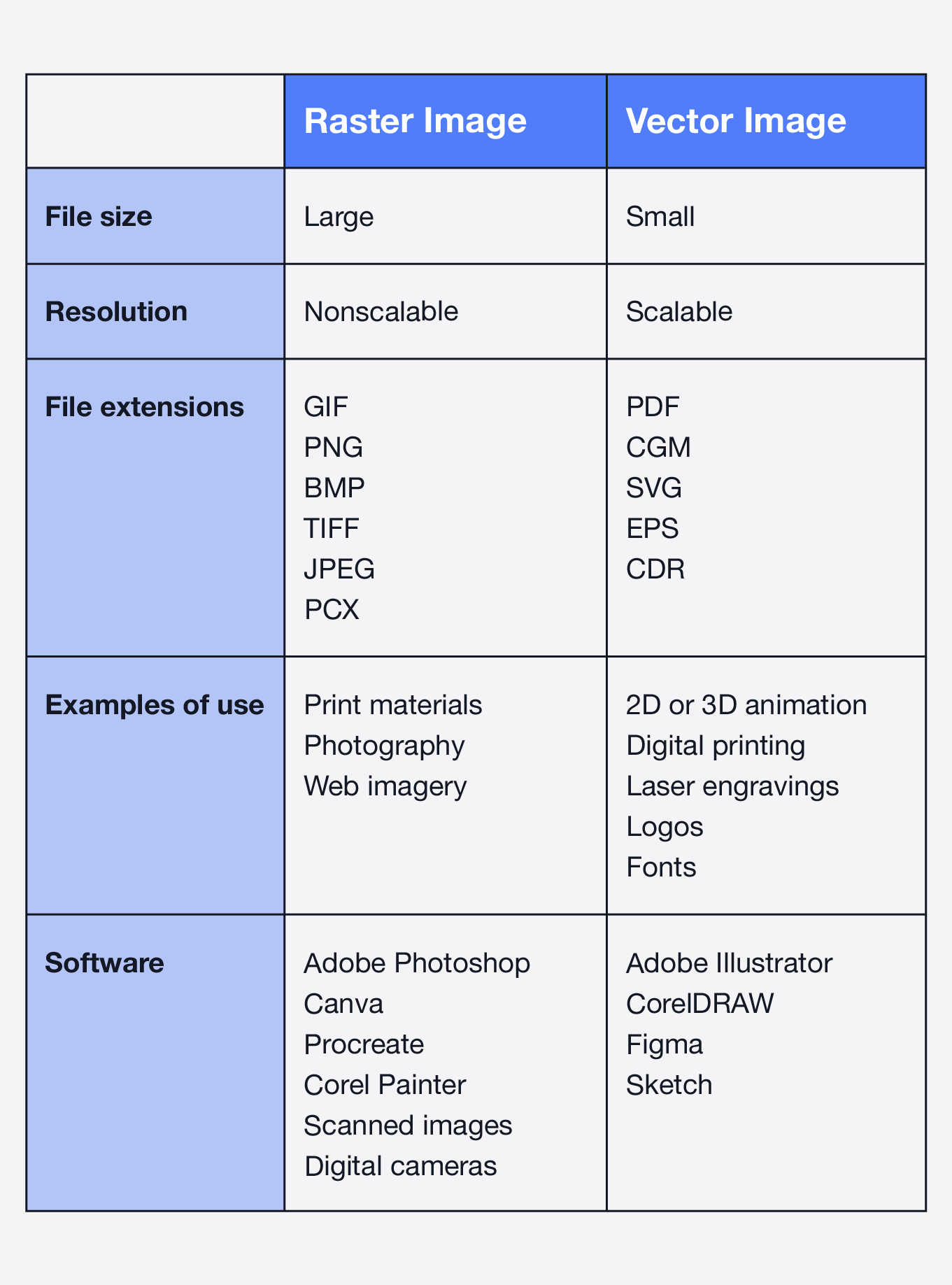
Vector and raster file formats have different uses in design and photography. Raster file formats are more commonly used in photography, whereas vector images are more commonly used in digital design.
Each file format has its own set of common file extensions. With raster files, you’ll typically use extensions like GIF, JPEG and PNG. With vector files, you’ll use extensions like PDF and SVG.
What Is a Raster Image?
Raster images are made up of a fixed number of pixels that determine the resolution quality of the image. When a photographer takes a picture with their camera, the image is built out in pixels. The more pixels an image has, the higher the resolution is. Raster images can easily become blurry when expanded and aren’t typically scalable.
With that, the more pixels an image has the larger the file is. Because of their size, raster file formats are more often used in photography and print materials.
To edit raster images, you must use raster-based programs or plug-ins like this PowerPoint add-in to edit your raster icons.
Design Tip: To cut down your file size for online photos, reduce your resolution to 72 PPI.
What Is a Vector Image?
Vector images, also known as scalable vector graphics, are made up of anchored curves, lines and dots that are instrumented by mathematical formulas created through design software.
With these mathematical formulas, vector images are infinitely scalable. They can be set at any resolution without losing quality. Vector graphics are device-independent, so resolution quality doesn’t depend on your computer screen’s pixels or dots in your printer. Since they’re made up of lines and dots, the file size is relatively small compared to raster files.
Vector file formats can be used for different digital design purposes, like animation and logo design. To edit vector images, you must use vector-based programs, like Sketch or Adobe Illustrator.
Design Tip: If you want to create a logo to use on different sized displays, create it using a vector file for better scalability.
Pros and Cons of Raster Images
Knowing the pros and cons of raster formatted images can help you decide why you might want to choose this file format over vectorized files.
Pros:
- Works best for print materials and digital photographs
- Ability to edit images
- Ideal for projects that use complex color blending
- More shareable and accessible on different design programs
- Easier to view online and available in more common file formats
Cons:
- Can be a relatively large file format
- Not easily scalable with a pixelated format
Pros and Cons of Vector Images
Let’s learn the pros and cons of vector formatted images and why you may choose to create your designs using vector files versus raster files.
Pros:
- Works best for digital printing and smaller designs
- Works best for scalable shapes and solid colors
- Can be compressed without loss of quality
- Smaller file size
- Easy to raster
Cons:
- Not as easily shareable or accessible as raster images
- Not ideal for photography
How To Convert Raster to Vector
While knowing when to use which graphic type is important, it can be easily as important to know how to convert raster graphics to vector and vice versa. Images with simple designs, like repetitive patterns, are the easiest to convert versus detailed graphics. Below are a few steps you can use if you have a rasterization project.
- Using Adobe Illustrator Image Trace: Adobe Illustrator is the most recommended program to use when converting a raster to a vector, because it only takes a few easy steps.
- Open up a new file in Illustrator and place your graphic onto the artboard using Shift + Command + P.
- Open up the Image Trace panel with Window > Image Trace.
- When you’re in the Image Trace panel, set both Colors and Mode to Color to 30.
- After the graphic is processed, expand the graphic with Object > Expand. You will now have editable vector components.
- Using other online resources: If you don’t have access to Adobe Illustrator, you can use other online resources to convert your image from raster to vector.
How To Convert Vector to Raster
Knowing how to convert vector graphics into raster file formats is another great technique to have in your design pocket. Here’s how you convert vector images into a raster file with two simple steps.
- Using Adobe Illustrator: This program is just as easy to use for converting a vector image to a raster file.
- Go to File > Export > Export As.
- From there, you can choose to convert your graphic to a TIFF, PNG or JPG file.
Now that you’ve learned the basics about vectors and rasters you can create any detailed logo or photograph without questioning the difference between raster vs. vector file formats.
Need a little inspiration to practice your vectorization skills? Check our icon collection to spark your next design project!